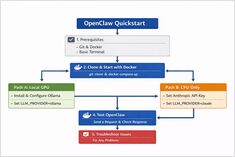
OpenClaw Quickstart: Install with Docker (Ollama GPU or Claude + CPU)
Install OpenClaw locally with Ollama
OpenClaw is a self-hosted AI assistant designed to run with local LLM runtimes like Ollama or with cloud-based models such as Claude Sonnet.

Install OpenClaw locally with Ollama
OpenClaw is a self-hosted AI assistant designed to run with local LLM runtimes like Ollama or with cloud-based models such as Claude Sonnet.

OpenClaw AI Assistant Guide
Most local AI setups start the same way: a model, a runtime, and a chat interface.

Comparison of Chunking Strategies in RAG
Chunking is the most under-estimated hyperparameter in Retrieval ‑ Augmented Generation (RAG): it silently determines what your LLM “sees”, how expensive ingestion becomes, and how much of the LLM’s context window you burn per answer.

From basic RAG to production: chunking, vector search, reranking, and evaluation in one guide.

Control data and models with self-hosted LLMs
Self-hosting LLMs keeps data, models, and inference under your control-a practical path to AI sovereignty for teams, enterprises, nations.

January 2026 trending Python repos
The Python ecosystem this month is dominated by Claude Skills and AI agent tooling. This overview analyzes the top trending Python repositories on GitHub.

January 2026 trending Go repos
The Go ecosystem continues to thrive with innovative projects spanning AI tooling, self-hosted applications, and developer infrastructure. This overview analyzes the top trending Go repositories on GitHub this month.

Testing Cognee with local LLMs - real results
Cognee is a Python framework for building knowledge graphs from documents using LLMs. But does it work with self-hosted models?

Thoughts on LLMs for self-hosted Cognee
Choosing the Best LLM for Cognee demands balancing graph-building quality, hallucination rates, and hardware constraints. Cognee excels with larger, low-hallucination models (32B+) via Ollama but mid-size options work for lighter setups.

Build AI search agents with Python and Ollama
Ollama’s Python library now includes native OLlama web search capabilities. With just a few lines of code, you can augment your local LLMs with real-time information from the web, reducing hallucinations and improving accuracy.

Pick the right vector DB for your RAG stack
Choosing the right vector store can make or break your RAG application’s performance, cost, and scalability. This comprehensive comparison covers the most popular options in 2024-2025.

Build AI search agents with Go and Ollama
Ollama’s Web Search API lets you augment local LLMs with real-time web information. This guide shows you how to implement web search capabilities in Go, from simple API calls to full-featured search agents.

Compare the best local LLM hosting tools in 2026. API maturity, hardware support, tool calling, and real-world use cases.
Running LLMs locally is now practical for developers, startups, and even enterprise teams.
But choosing the right tool — Ollama, vLLM, LM Studio, LocalAI or others — depends on your goals:

Deploy enterprise AI on budget hardware with open models
The democratization of AI is here. With open-source LLMs like Llama 3, Mixtral, and Qwen now rivaling proprietary models, teams can build powerful AI infrastructure using consumer hardware - slashing costs while maintaining complete control over data privacy and deployment.

LongRAG, Self-RAG, GraphRAG - Next-gen techniques
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has evolved far beyond simple vector similarity search. LongRAG, Self-RAG, and GraphRAG represent the cutting edge of these capabilities.

Cut LLM costs by 80% with smart token optimization
Token optimization is the critical skill separating cost-effective LLM applications from budget-draining experiments.